AR in Healthcare Industry
Consequently, next-generation technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), etc. are making inroads into the domain of healthcare to improve patient care, make it more affordable, and help medical professionals to make themselves more flexible, agile and highly responsive. Now with these new technologies in place, healthcare professionals can make sound decisions in critical situations without making any grave errors.
Amongst these emerging technologies, AR has struck a chord with the healthcare community, leading the forefront in surgical assistance, AR medical training for medical students, patient care, and more.
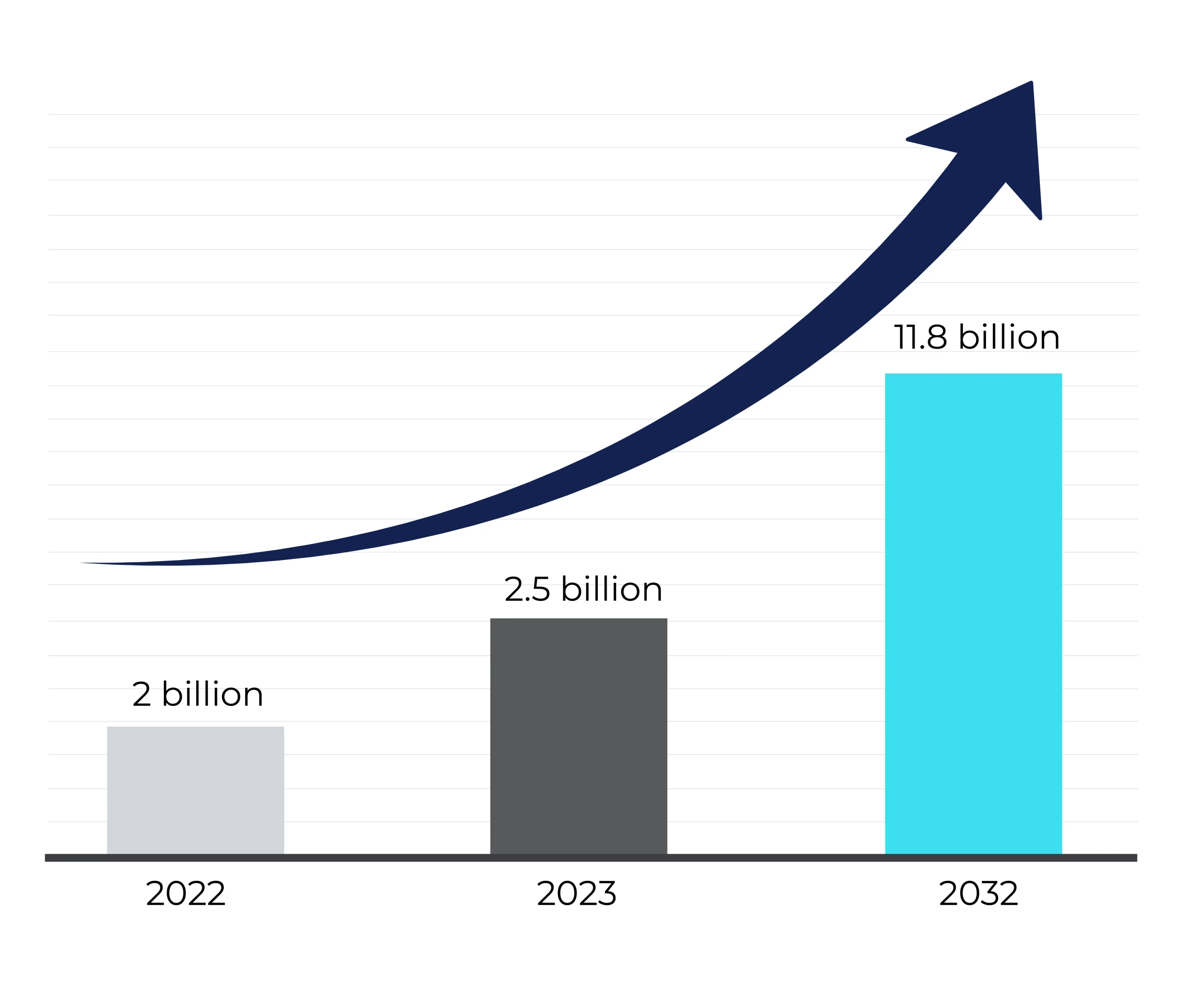
According to the Market Research Future report, augmented reality in healthcare was valued at USD 2.0 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow from USD 2.5 Billion in 2023 to USD 11.8 billion by 2032.
Understanding Augmented Reality
AR technology allows the superimposing of digital elements such as 3D models, images, videos, or text onto the real-world environment in a way that gives the feel that the content is physically there, essentially merging the digital and the physical worlds. For AR to work, camera-equipped hardware such as wearable smart glasses or heads-up displays are required. But that just is not it, the smartphones of today are very well equipped with GPS, accelerometers, and sensors required for the AR solution to work, making the technology more popular mainstream.
AR technology is seamlessly interwoven into our lives, whether we are aware of it or not. Well, take a moment and think about the Snapchat or Instagram filters of the bunny ears or the crying face that we use in our social media photos; they are an example of AR. Remember the very viral phenomenon of Pokemon Go, that again is AR. Consider this, if you are thinking of purchasing a sofa from Amazon or IKEA, you can now use your smartphone to get the digital image of the sofa in the real world to see how the particular sofa would fit in your real world. You can interact with the 3D model of the sofa as you please, you can zoom in, zoom out, assemble, dismantle, etc, move around, try placing it in different places, and see the perfect spot for the sofa. This helps a customer to make a wise decision before making a purchase. Try doing a simple Google search of dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus, and AR can bring Tyrannosaurus to your room, for this, all you need is your phone. From trying out different shades of makeup to training medical students, the possibilities AR has are endless.
To know the origins of AR, we need to take a step back and travel back to the 1960s to see how the concept of AR came into being. It was then that a computer scientist named Ivan Sutherland developed the first head-mount display (HMD) system known as the “Sword of Damocles”. However not until the 20th century did AR gain attention, most of it due to the widespread availability of smartphones such as the iPhone, that pushed AR to the mainstream. Of all the industries, it was the retail sector that early adopted the technology to improve their customer experience. As consumers were able to experience it on their smartphones with no fuss of having a headset on hand, it increased its popularity and slowly expanded its wings and extended to healthcare, where the technology continues to make impactful contributions.
Unlike its very popular counterpart, Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users into a digital world that is computer-generated, completely taking them away from the physical world, which is very different from what AR does, unlike that AR brings digital content into your physical world. This is the basic difference that distinguishes both technologies. In order to experience VR, users need to get their hands on VR headsets such as Meta Quest devices, HTC Vive, and many more in the market. You might have seens games strapping on the VR headsets and immersing themselves in the game world and playing passionately.
Mixed Reality (MR) on the other hand, is very similar to AR. MR allows digital content to be overlaid in the physical world but offers more complex interactions than AR. Most often, people interchange with AR and MR but keep note that all AR is MR, but not all MR are AR. Most people call MR as AR 2.0 as they both consist of virtual objects on top of a physical world. The popular devices one can use to experience MR include Microsoft Hololens, Magic Leap, etc.
How does Augmented Reality work?
CAMERA AND SENSORS:
To see and understand the physical world in the areas where the AR elements will be placed, cameras and sensors work to track and map the environment and also sense the conditions of the environment and project that onto our digital world to give the most accurate view.
AR PROCESSOR:
Like a computer’s CPU, an AR processor, handles all the real-time data from the sensors and the camera feed to accurately place the virtual content within the physical world.
AR SOFTWARE:
The software is the soul of the system enabling the creation and managing of augmented content by analyzing the data from the cameras and the sensors.
CONTENT:
The content for an AR application includes 3D models, videos, text, and other digital information that are overlaid onto the real world.
CONNECTIVITY:
Internet or network connection to enable cloud-based processing, data retrieval, and real-time updates, especially for complex or collaborative AR experiences.
INTERACTIVITY:
The UI interface allows users to interact with AR content through touch inputs or gestures, voice commands, etc.
TRACKING SYSTEM:
Technology that tracks the user's position and orientation in the real world, ensuring the accurate alignment of virtual elements with the physical environment.
DISPLAY DEVICE:
wearable smart glasses such as AR glasses, or smartphones, to visualize digital content.
The Growing Adoption of AR in Healthcare
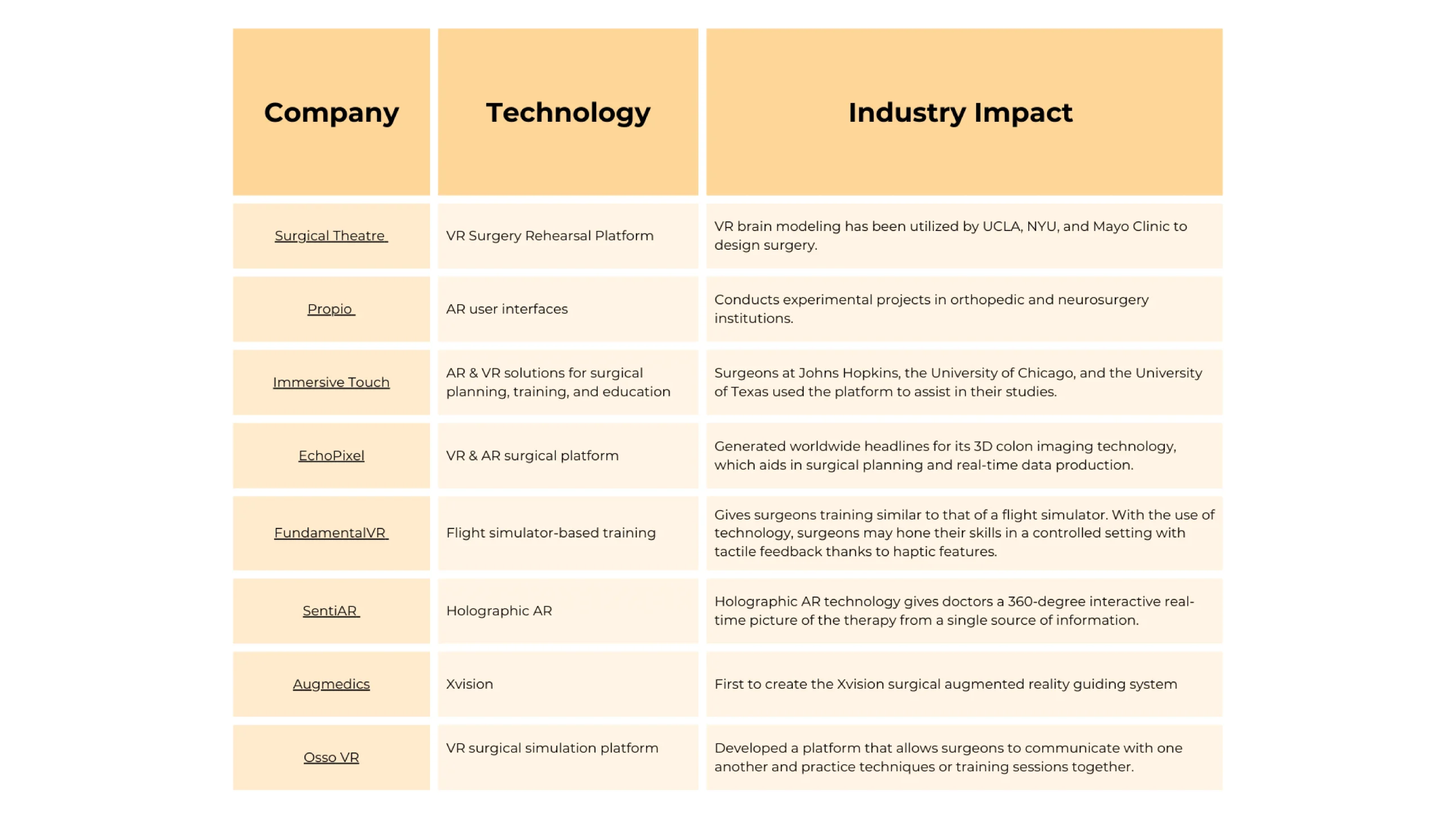
Here’s a list of a few companies investing in the healthcare sector, along with some major market players making waves in healthcare.
Use Cases of AR in Healthcare
In surgery, AR can overlay critical information on the patient’s body or the surgical field to help surgeons with real-time data or 3D models of anatomical structures, surgical instruments, etc. AR can help in real-time assistance by providing step-by-step instructions on procedures thereby reducing several human errors. Surgeons can train their assistants using AR for pre-surgery training for hands-on practice and rehearsal of the procedure so that the juniors are well-equipped to work under the surgeon without causing any mistakes. AR can also assist in documenting the procedure with images and videos of the entire procedure that can be used for reviews and training purposes after the procedure.
Imagine a scenario where a patient requires immediate surgery beforehand and the expert for the surgery is unavailable. In critical situations like this, AR can provide remote assistance capabilities where the expert can join in on the surgery and guide the surgeons in real-time irrespective of the location. The expert can collaborate with the surgeons in real-time and can provide real-time annotations and other visual aids that can further help the surgeons to successfully complete the procedure.
Training is another area in which AR finds real importance. With its ability to overlay the 3D models into the physical space, AR can bring to life the different training solutions required to train medical students or for other training. AR enables the learners to explore the 3D models of human anatomy, from the workings of the heart, lungs, and different parts of the body to the impact of drugs, the effect it has, the impact in case of any allergies or medical conditions like diabetes, etc. Providing a visual understanding can help the students understand the concepts better and refine their techniques. AR can provide a customized learning opportunity based on the specific field or based on the needs of the individual even without an instructor in place, as the solution can provide textual, audio, and video descriptions that provide more awareness to the learner.
AR can be very efficiently used for mental health therapy, particularly in treating phobias, trauma triggers, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). AR-enabled therapy can work as a safe environment to simulate situations related to the patient’s phobias by gradually exposing them to their fears and helping them to cope parallelly. Along with this, AR can also help therapists to monitor the reactions of the patient and can adjust the solution accordingly. AR solutions can be an engaging way to build confidence in the patients with many interesting activities to ease their fear psychologically alongside the real treatment.
AR can be integrated to help and train medical practitioners and patients in operating their medical devices by providing step-by-step instructions on operating, assembling, and even using various medical instruments. AR can provide interactive guidance by overlaying instructions, videos, texts, animations, and more to make the users understand the procedure before using a real device. This can be considered as an alternative for lengthy manuals with the smallest readable fonts. It also aids in reducing mistakes that can damage the devices. With the visual guidance in place, the possibility of making a mistake is too low.
In dentistry, AR can assist in procedures, helping the dentists by overlaying digital guides on the patient’s mouth, making sure that the dental tools or implants or another requirement for the procedure is placed precisely. AR can also overlay X-ray images or previous diagnostic data over the patient's mouth to understand the history of procedures the patient has done and can also help in real-time during a procedure. AR can also be used for post-procedure care, where the patients themselves can use an AR to see how they should be maintaining, cleaning, or taking out their various dental appliances. There is also a possibility for remote monitoring where the dentists can help the patients if there are any uncomfortable moments with the new procedure or they can see if there’s an issue, etc without going to the dentist in person.
AR finds its use in drug information visualization. Pharmacists and doctors can use AR for patient counseling, medical management, etc. Inpatient counseling, the AR-based solutions can provide 3D representations of the particular drug interacting with specific biological targets, such as enzymes or receptors, making the patient understand how the drug works. The solution can also be used for personalized drug management, where doctors can show patients the drug to use based on patient-specific data, and based on that, the solution can show the effect the drug has. For example, if a patient has diabetes, the doctor can show the effect of the drug on the blood glucose levels. It can also produce the potential side effects the drug may have based on the patient-specific data. Doctors can also train the new medical students with AR overlays that provide step-by-step visualizations of how the medication should be administered. The instructions mentioned on the cover of the back of the drug can be visualized in AR before administration for better understanding. This can also help the patients themselves if they are administering the drugs by themselves. This helps them to take proper care and administer the drug properly. With AR in drug visualization, educators can teach the students step-by-step instructions on drug interactions with virtual scenarios and simulations to see the effect of the drugs on human systems to enhance their learning experience.
Real-Life Applications of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Surgical Assistance with AR
A real-life experience of AR in surgical assistance was by Xvision by Augmedics. The system provides surgeons the power to see patients' anatomy as if they have “x-ray vision”, and accurate navigation of instruments and implants during spine surgery. The AR device is a wireless device that comes with a built-in tracker and retinal display that enables surgeons to keep their eyes directly on the patient. The device provides a 3D visualization and assists in instrument location and trajectory planning, helping in the real-time navigation of instruments and implants. The surgeries have been done with a 99.1% accuracy of overall percutaneous and screw placement. The platform is compatible with most of the surgical tools and systems out there. Allows for the visualization of the cortical edge with the transparent 3D view option. This solution gives an insight into the potential of AR in surgical assistance.
Vein Visualization with AR
Most often, finding veins is difficult for people with darker skin tones. In order to ease this, AccuVein has come up with an AR system to help clinicians visualize veins to quickly locate the veins which otherwise are very difficult to find. The vein visualization improves accuracy, making procedures like blood draws and IV placements more efficient and easy rather than done traditionally, as the AR solution provides the details such as the locations, depth, and size, this can, in turn, help the clinicians from making multiple insertions. The patient on the other hand is free from the torture of needle pricking.
AR for Medical Training
AR can assist medical students in surgical training and in subject-level learning. AR can provide 3D modules on different modules in the curriculum that help the learners visualize the 3D images of various anatomical structures, step-by-step instructions on complex procedures, and pre-surgery training for junior surgeons to give an insight into real-life surgery.
AR for Dental Care
In dentistry, AR solutions can provide a visualization of various dental procedures, which gives the patients an idea of how the procedure will be and can also see the output beforehand, allowing for precise treatment planning and patient consultations. In the dental solutions by Kapanu, AR has a special place that allows realistic 3D visualization of various dental procedures, a virtual mock-up of the outcome with any number of options for the patient to choose from, along with the dynamic modification opportunity in real-time to instill confidence in the patient to go ahead with the procedure.
Innovative Strategies for Tomorrow
Let’s briefly explore how AI and IoMT will aid healthcare in this new era.
AI Integrations and IoMT
AI IntegrationsAI Market Growth: The global AI in healthcare market was estimated at USD 19.27 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 38.5% from 2024 to 2030. AI adoption in healthcare is rapidly increasing, with 79% of healthcare organizations using AI technology. Organizations are seeing a return on AI investments within 14 months, with an average return of $3.20 for every $1 invested. Disease Detection: AI is widely used in detecting early-stage cancers and other life-threatening diseases. For example, AI enables the review of mammograms 30 times faster with 99% accuracy, reducing false positives and unnecessary biopsies. AI-based devices are also being used for early detection of heart diseases and lung cancers, allowing for immediate patient care. Drug Research: AI accelerates drug research by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify potential outcomes, speeding up the research process and saving lives by predicting potential drug efficacy and safety. |
IoMTMarket Growth: The global IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) market size was USD 47.32 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 814.28 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 38.5%. Wearable Devices: IoMT includes wearable, implanted, and stationary medical devices that enable remote monitoring of vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. This technology supports at-home patient monitoring, reducing frequent hospital visits and improving chronic disease management. Patient Management: IoMT enhances patient care by streamlining routine tasks and automating processes, minimizing human errors in diagnosis. It has the potential to revolutionize patient care, diagnosis, and post-treatment management. |
Boost Your AR Strategies with Us
At TA, our expertise spans a wide range of domains such as Defence and Space, Health and Wellness, the Oil and Gas industry, and Aviation. Our development capabilities range from AR/VR Apps, AR/VR Training and Learning Solutions Development, Live and On-demand Video Streaming, Location-based AR navigation and routing applications, 3D Design and Development, etc. From AR VR cadet training solutions for India’s premier training institution, AR-based golf and basketball solutions, AR e-commerce applications, VR and Metaverse-based heavy machinery training, VR Subsea engineering training, Clinical and Rehabilitation training solutions in VR, and more, our team can make any of your requirements come to life.
Key Projects By Travancore Analytics
The AR Medical Training solution contains modules on different parts of human anatomy and provides a 3D overlay of a particular part. Take, for example, a module in human psychology, and the students are taught about the skeletal system. To experience the content, the students can wear the desired AR headset, and irrespective of the location they are in, they can join and interact with the AR model of a skeleton. Further, they can collaborate with one another and try dismantling the skeleton, such as taking each bone and getting a detailed analysis of what each part is with a textual description of what part. Additionally, there’s a voice and video option to further knowledge of what the part is, its importance, and how to identify the part.
With the solution in place, students could team up and learn the vital details without causing real-life damage that can happen when studying real-life skeletons; it can damage the skeleton in real life. This can be avoided, and instead, the students can be provided with a better understanding of each part and can be learned even without the aid of an instructor.
The features of the solution include:
-- Real-time collaboration irrespective of the place and time
-- Textual and audio descriptions
-- Better knowledge retention
-- Self-learning modules to learn without the aid of an instructor
With the rising number of diseases and the skyrocketing medical costs, affordable and accessible treatment has become the need of the hour. In response to these challenges, the healthcare sector is ushering in leading-edge technologies such as AR, VR, AI, IoT, and more into its horizon.
Amongst all these emerging technologies, AR has successfully managed to address many of the pressing challenges that the sector faced. As AR continues its transformative journey to innovate the technology landscape, we can anticipate a growing number of effective and practical solutions unfolding in the healthcare sector. These advancements promise to transform the healthcare sector with improved medical practices, making healthcare accessible and affordable for everyone, and opening up new venues that were earlier just stuff in sci-fi movies.
With the integration of AR with AI/ML, IoT, and other cutting-edge technologies, the healthcare industry is further set to expand the horizons of healthcare. With this rapid pace of technological advancements, it’s a matter of time before technologies can be affordable and accessible to all people with personalized use rather than even going to the hospital for medical needs. Let’s wait and see how these developments shape the future of healthcare.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions You May have on Augmented Reality and Healthcare
Augmented Reality (AR) comes under the umbrella of Spatial Computing technologies, which include VR, MR, Metaverse, and Digital Twin. Among these, AR technology enables the overlay of digital content such as texts, images, videos, etc., onto the physical environment where the user can interact with these in real life. In the current technology landscape, AR is making significant strides in the domain of healthcare. The healthcare sector is increasingly leveraging AR technologies to improve the quality of treatments, patient care, the well-being of healthcare personnel, and more. From real-time and remote surgical assistance to medical training and mental health assistance, the real-life applications of AR in healthcare are endless. Recognizing the impact of AR in healthcare, many prominent organizations are also investing heavily in the sector. Furthermore, AR can also be easily integrated into other technologies, such as AI, IoT, Robotics, and more, further expanding the potential to assist the healthcare sector further.
The healthcare industry is increasingly exploring cutting-edge technologies and has found a strong interest in AR technologies, recognizing its significant impact on the sector. According to the Market Research Future report, augmented reality in healthcare was valued at USD 2.0 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow from USD 2.5 billion in 2023 to USD 11.8 billion by 2032. The healthcare sector is adopting AR technologies for procedures that were once considered impossible, such as complex spinal surgery procedures, to medical training. Recognizing the potential implications AR has on the domain, many tech giants such as Google, Microsoft, Siemens, and Apple, as well as newer players such as Surgical Theater, Propio, Osso VR, EchoPixel, etc., are also heavily investing in AR technology in healthcare.
AR is transforming the various facets of healthcare, making treatments more efficient, improving medical training, and enhancing patient care. Some of the use cases of AR include real-time and remote surgical assistance, medical training, dental care, and mental health rehabilitation.
AR solutions can serve as powerful assistive technologies for mental health and wellness practices, rehabilitation assistance, and more, providing additional support and accessibility for patients. For instance, AR can help patients with trauma and PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder) by providing exposure therapy that makes physical environments more accessible by adding virtual elements that can trigger or induce anxiety that are brought into a safe environment, helping the patient address the triggers. According to the FDA, AR, and VR technologies can provide additional comfort to patients by allowing them to participate in specific therapies from the comfort of their own homes rather than in a hospital or other clinical setting. The thought is that VR and AR could widen accessibility to some treatments.
There is an increasing number of applications of AR in healthcare. The main area where AR finds its best use is in surgery assistance planning and medical training. In surgery assistance, surgeons can use AR to see the patient’s anatomy and work on the accurate navigation of instruments, trajectory planning, and more. Along with visualization of the entire anatomy of the patient, surgeons can use AR to preplan the surgery and give training to prepare the team before the surgery, preventing any major mishap at the time of the surgery. AR also enables remote surgery, where, in case of emergency situations where the main surgeon cannot be at the place in real-time, remote collaboration can be done. Along with that, AR also opens the doors for training medical students, providing them with subject-level training and helping the students with 3D models of various anatomical structures where they can assemble and dismantle these structures, which can also come with textual, audio, and video descriptions. These are two of the primary areas in which AR finds its impactful use in the healthcare sector.
